
1、I/O是什么?
I/O 是Input/Output(输入、输出)的简称,输入流可以理解为向内存输入,输出流是从内存输出。
2、流
流是一个连续的数据流,可以从流中读取数据,也可以往流中写数据。流与数据源,或数据源流向的媒介相关联。
在Java IO流中,流可以是字节流,也可以是字符流。
3、Java I/O 用途与对应的流一览
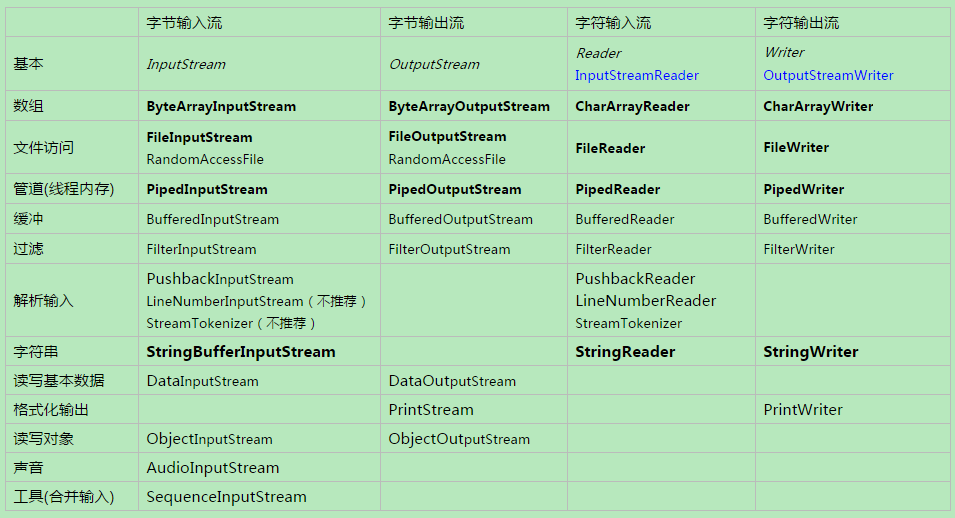
注:粗体为节点流。蓝色为转换流(字节流转为字符流)。
4、流的处理
流分节点流和处理流两种。
节点流:可以从或向一个特定的地方(节点)读写数据。如FileInputStream、FileReader。
处理流:是对一个已存在的流的连接和封装,通过所封装的流的功能调用实现数据读写。如BufferedReader.处理流的构造方法总是要带一个其他的流对象做参数。一个流对象经过其他流的多次包装,称为流的链接
5、文件访问
(1)读取文件
如果你需要在不同端使用读取文件,你可以根据你要读的文件是二进制文件还是文本文件,或者根据你要处理的数据是准备采取字节方式还是字符方式,决定使用 FileInputStream 或者 FileReader。两者支持你从文件开头开始到文件结尾读取一个字节或者字符,也可以将读取的多个字节或字符,写入到内存的字节数组或字符数组。
单字节读取文件示例:
public static void readFileAsByte() throws IOException { String filepath = "file.bin"; java.io.InputStream is = null; try { is = new FileInputStream(filepath); int data = -1; while ((data = is.read()) != -1) {// -1 表示读取到达文件结尾 //操作数据 System.out.print((byte)data + " "); } } finally { if (is != null) { is.close();// 关闭流 } } } 字节数组读取文件示例:
public static void readFileAsByteArray() throws IOException { String filepath = "file.bin"; java.io.InputStream is = null; try { is = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(filepath));// 组装BufferedInputStream流,加入缓冲能力 byte[] data = new byte[256]; int len = -1; while ((len = is.read(data)) != -1) {// -1 表示读取到达文件结尾 //操作数据 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { System.out.print(data[i] + " "); } } } finally { if (is != null) { is.close();// 关闭流 } }} 单字符读取文件示例:
public static void readFileAsChar() throws IOException { String filepath = "file.txt"; java.io.Reader r = null; try { r = new FileReader(filepath); int data = -1; while ((data = r.read()) != -1) {// -1 表示读取到达文件结尾 //操作数据 System.out.print((char) data); } } finally { if (r != null) { r.close();// 关闭流 } }} 字符数组读取文件示例:
public static void readFileAsCharArray() throws IOException { String filepath = "file.txt"; java.io.Reader r = null; try { r = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filepath));// 组装BufferedReader流,加入缓冲能力 char[] data = new char[256]; int len = -1; while ((len = r.read(data)) != -1) {// -1 表示读取到达文件结尾 //操作数据 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { System.out.print(data[i]); } } } finally { if (r != null) { r.close();// 关闭流 } }} (2)写入文件
与读取文件类似:
如果你需要在不同端使用写入文件,你可以根据你要写的文件是二进制文件还是文本文件,或者根据你要处理的数据是准备采取字节方式还是字符方式,决定使用 FileOutputStream 或者 FileWriter。两者支持你可以一次写入一个字节或者字符到文件中,也可以直接写入一个字节数组或者字符数据。数据按照写入的顺序存储在文件当中。
单字节写入文件示例:
public static void writeFileAsByte() throws IOException { String filepath = "file.bin"; java.io.OutputStream os = null; try { os = new FileOutputStream(filepath); os.write('1'); os.write('2'); os.write('3'); os.write('4'); os.flush();// 把缓冲区内的数据刷新到磁盘 } finally { if (os != null) { os.close();// 关闭流 } }} 字节数组写入文件示例:
public static void writeFileAsByteArray() throws IOException { String filepath = "file.bin"; java.io.OutputStream os = null; try { os = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(filepath)); // 模拟 byte[] data = new byte[256]; new Random().nextBytes(data); os.write(data); os.flush();// 把缓冲区内的数据刷新到磁盘 } finally { if (os != null) { os.close();// 关闭流 } } } 单字符写入文件示例:
public static void writeFileAsChar() throws IOException { String filepath = "file.txt"; java.io.Writer w = null; try { w = new FileWriter(filepath); w.write('1'); w.write('2'); w.write('3'); w.write('4'); w.flush();// 把缓冲区内的数据刷新到磁盘 } finally { if (w != null) { w.close();// 关闭流 } }} 字符数组写入文件示例:
public static void writeFileAsCharArray() throws IOException { String filepath = "file.txt"; java.io.Writer w = null; try { w = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(filepath));// 组装BufferedWriter流,加入缓冲能力 // 模拟 char[] data = new char[256]; String f = "0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"; Random rd = new Random(); for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) { data[i] = f.charAt(rd.nextInt(f.length())); } w.write(data); w.flush();// 把缓冲区内的数据刷新到磁盘 } finally { if (w != null) { w.close();// 关闭流 } } } (3)随机访问文件
如果你需要不按特定的存取顺序,随意读取或者写入文件,可以考虑RandomAccessFile。
void seek(long pos) 设置到此文件开头测量到的文件指针偏移量,在该位置发生下一个读取或写入操作。
简单示例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { RandomAccessFile file = null; try { file = new java.io.RandomAccessFile("file.bin", "rw"); file.seek(0); file.writeChar('1'); file.seek(0); System.out.println(file.readChar()); /** * 读取 */ int data = -1; while ((data = file.read()) != -1) {// -1 表示读取到达文件结尾 //操作数据 System.out.print((byte)data + " "); } } finally { if (file != null) { file.close();// 关闭流 } } }
6、管道(线程内存)
管道为同一JVM中运行的线程提供基于内存的通信机制。但是你不能利用管道在不同的JVM中的线程间通信。
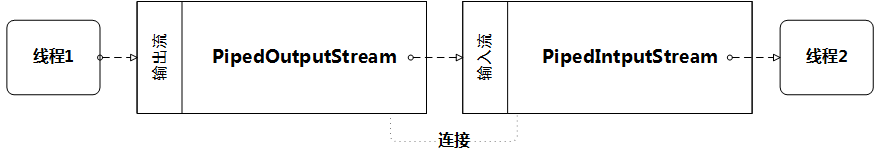
在概念上,Java的管道不同于Unix/Linux系统中的管道。在Unix/Linux中,运行在不同地址空间的两个进程可以通过管道通信。在Java中,通信的双方应该是运行在同一进程中的不同线程。当然除了管道之外,一个JVM中不同线程之间还有许多通信的方式。实际上,线程在大多数情况下会传递完整的对象信息而非原始的字节数据。但是,如果你需要在线程之间传递字节数据,Java IO的管道是一个不错的选择。
当使用两个相关联的管道流时,务必将它们分配给不同的线程。read()方法和write()方法调用时会导致流阻塞,这意味着如果你尝试在一个线程中同时进行读和写,可能会导致线程死锁。
简单示例:
static class Input implements Runnable { private final PipedInputStream inputStream = new PipedInputStream(); public Input() { } public PipedInputStream getInputStream() { return inputStream; } @Override public void run() { try { byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; int len = -1; System.out.println("管道读取准备。"); StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer(); while ((len = inputStream.read(buf)) > 0) { //System.out.println(new String(buf, 0, len)); result.append(new String(buf, 0, len)); } System.out.println("管道读取结果:" + result.toString()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if (inputStream != null) inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } static class Output implements Runnable { private final PipedOutputStream outputStream = new PipedOutputStream(); public Output() { } public PipedOutputStream getOutputStream() { return outputStream; } @Override public void run() { try { System.out.println("管道写出准备。"); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); // 模拟 通过for循环写入2050个字节 for (int i = 0; i < 201; i++) { sb.append("0123456789"); if (i > 0 && (i % 10 == 0)) { sb.append("\r\n"); } } String str = sb.toString(); outputStream.write(str.getBytes()); System.out.println("管道写出完成。"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if (outputStream != null) outputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Input input = new Input(); Output output = new Output(); /** * 将“管道输入流”和“管道输出流”关联起来。 */ //input.getInputStream().connect(output.getOutputStream());// 与下面一行等价 output.getOutputStream().connect(input.getInputStream()); new Thread(input).start(); new Thread(output).start(); }
7、序列化与ObjectInputStream、ObjectOutputStream
使用ObjectInputStream、ObjectOutputStream读取或写入对象,首先该对象必须实现Serializable接口,使得能够序列化和反序列化。
简单示例:
@SuppressWarnings("unused") public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { class A implements java.io.Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -9115696482036699559L; private int i = 1; private float f = 3; private String s = "风策信"; public A() { super(); } public A(int i, float f, String s) { super(); this.i = i; this.f = f; this.s = s; } @Override public String toString() { StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); builder.append("A [i=").append(i).append(", f=").append(f).append(", s=").append(s).append("]"); return builder.toString(); } } class B implements java.io.Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 6124575321340728225L; private long i = 2; private double f = 4; private String str = "风策信"; public B() { super(); } public B(long i, double f, String str) { super(); this.i = i; this.f = f; this.str = str; } @Override public String toString() { StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); builder.append("B [i=").append(i).append(", f=").append(f).append(", str=").append(str).append("]"); return builder.toString(); } } A a = new A(1, 3, "a"); B b = new B(2, 4, "b"); //System.out.println(a); //System.out.println(b); ObjectOutputStream oos = null; try { oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("object.data.bin")); oos.writeObject(a); oos.writeObject(b); oos.flush();// 把缓冲区内的数据刷新到磁盘 } finally { if (oos != null) oos.close(); } ObjectInputStream ois = null; try { ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("object.data.bin")); A a1 = (A) ois.readObject(); B b1 = (B) ois.readObject(); System.out.println(a1); System.out.println(b1); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (ois != null) ois.close(); } }
8、回推流:PushbackInputStream与PushbackReader
PushbackInputStream/PushbackReader 用于解析InputStream/Reader内的数据,允许你读取字节/字符后,回推(pushback)到流中,而不破坏流。
PushbackInputStream类具有以下构造函数:
PushbackInputStream(InputStream inputStream)PushbackInputStream(InputStream inputStream,int numBytes)
第一种形式创建的流对象允许将一个字节返回到输入流; 第二种形式创建的流对象具有一个长度为numBytes的回推缓存,从而允许将多个字节回推到输入流中。
提供了unread()方法,如下所示:
void unread(int b)void unread(byte[] buffer)void unread(byte[] buffer,int offset,int numBytes)
第一种形式回推b的低字节,这会使得后续的read()调用会把这个字节再次读取出来。第二种形式回推buffer中的字节。第三种形式回推buffer中从offset开始的numBytes个字节。当回推缓存已满时,如果试图回推字节,就会抛出IOException异常。
示例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String filepath = "file.bin"; java.io.OutputStream os = null; try { os = new FileOutputStream(filepath); os.write('#'); os.write(new byte[]{'a', 'b', 'c', 'd'}); os.flush();// 把缓冲区内的数据刷新到磁盘 } finally { if (os != null) { os.close();// 关闭流 } } /** * 回推(pushback) */ PushbackInputStream pis = null; try { //pis = new PushbackInputStream(new FileInputStream(filepath)); pis = new PushbackInputStream(new FileInputStream(filepath), 3); int len = -1; byte[] bytes = new byte[2]; while ((len = pis.read(bytes)) != -1) { if ('b' == bytes[0]) { //pis.unread('U'); //pis.unread(bytes); pis.unread(new byte[]{'1', '2', '3'}); } for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { System.out.print(((char) bytes[i])); } } System.out.println(); } finally { if (pis != null) pis.close(); } /** * 会发现PushbackInputStream并没有改变目标介质的数据,不破坏流 */ try { pis = new PushbackInputStream(new FileInputStream(filepath)); int len = -1; byte[] bytes = new byte[2]; while ((len = pis.read(bytes)) != -1) { for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { System.out.print(((char) bytes[i])); } } } finally { if (pis != null) pis.close(); } } 注:PushbackInputStream对象会使得InputStream对象(用于创建PushbackInputStream对象)的mark()或reset()方法无效。对于准备使用mark()或reset()方法的任何流来说,都应当使用markSupported()方法进行检查。
9、行数记录:LineNumberInputStream与LineNumberReader
LineNumberInputStream与LineNumberReader提供跟踪行号的附加功能。行是以回车符 ('\r')、换行符 ('\n') 或回车符后面紧跟换行符结尾的字节序列。在所有这三种情况下,都以单个换行符形式返回行终止字符。 行号以 0 开头,并在 read 返回换行符时递增 1。
使用getLineNumber()可以获取当前读取所在行数。
示例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String filepath = "file.txt"; java.io.Writer w = null; try { w = new FileWriter(filepath); w.write("百世山河任凋换,一生意气未改迁。愿从劫火投身去,重自寒灰飞赤鸾。\r\n"); w.write("沧海桑田新几度,月明还照旧容颜。琴心剑魄今何在,留见星虹贯九天。 \n"); w.write("冰轮腾转下西楼,永夜初晗凝碧天。长路寻仙三山外,道心自在红尘间。 \n"); w.write("何来慧剑破心茧,再把貂裘换酒钱。回望天涯携手处,踏歌重访白云间。\n"); w.write("何以飘零去,何以少团栾,何以别离久,何以不得安? \n"); w.flush();// 把缓冲区内的数据刷新到磁盘 } finally { if (w != null) { w.close();// 关闭流 } } /** * LineNumberReader */ LineNumberReader lnr = null; try { lnr = new LineNumberReader(new FileReader(filepath)); int len = -1; char[] chars = new char[2]; //int lastLineNumber = -1; while ((len = lnr.read(chars)) != -1) { for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { System.out.print(((char) chars[i])); } /*int lineNumber = lnr.getLineNumber(); if (lineNumber != lastLineNumber) { System.out.println("---------------行数:" + lineNumber); lastLineNumber = lineNumber; }*/ } int lineNumber = lnr.getLineNumber(); System.out.println("行数:" + lineNumber); System.out.println(); } finally { if (lnr != null) lnr.close(); } }
10、StreamTokenizer的使用
StreamTokenizer定义了几种基本的常量用于标识解析过程:TT_EOF(流结尾)、TT_EOL(行结尾)、TT_NUMBER(数字符号, 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 . -都属于数字语法)、TT_WORD(一个单词)。
ttype 在调用 nextToken 方法之后,此字段将包含刚读取的标记的类型。 nval 如果当前标记是一个数字,则此字段将包含该数字的值。 sval 如果当前标记是一个文字标记,则此字段包含一个给出该文字标记的字符的字符串。public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { StreamTokenizer tokenizer = new StreamTokenizer(new StringReader("Sven had 7 shining ring...")); while (tokenizer.nextToken() != StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF) {// 流末尾 if (tokenizer.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_WORD) { System.out.println(tokenizer.sval); } else if (tokenizer.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_NUMBER) { System.out.println(tokenizer.nval); } else if (tokenizer.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_EOL) {// 行末尾 System.out.println(); } } //System.out.println(tokenizer.lineno());} 基本方法介绍一下:
nextToken() - 从此标记生成器的输入流中解析下一个标记。
(1)标记注释
commenChar(int ch) - 指定某个字符为注释字符,此字符之后直到行结尾都被stream tokenizer忽略。
slashSlashComments(boolean flag) - 如果为true,则/*与*/之间的都被认为是注释,反之,不是。
slashStartComments(boolean flag) - 如果为true,则//之后到行结尾的所有都被认为是注释,反之,不是。
(2)基本语义
eolIsSignificant(boolean flag) - 决定一个行结束符是否被当作一个基本的符号处理,如果是true,则被当作一个基本符号,不当作普通的分隔符,如果是false,则保持原义,即当作普通的分隔符。
lowerCaseMode(boolean flag) - 决定是否读取一个单词时是否转变成小写。
parseNumbers() - 当stream tokenizer遭遇到一个单词为双精度的浮点数时,会把它当作一个数字,而不是一个单词。
resetSyntax() - 重置语法表使所有的字符都被认为是“ordinary”。
(3)指定字符语义
ordinaryChar(int ch) - 指定字符在这个tokenizer中保持原义,即只会把当前字符认为普通的字符,不会有其他的语义。
ordinaryChars(int low, int hi) - 指定范围内的字符保持语义,同上whitespaceChars(int low, int hi) - 字符low与hi之间的所有字符都被当作为空格符,即被认识为tokenzier的分隔符。
wordChars(int low, int hi) - 字符low与hi之间的所有字符都被当作为单词的要素。一个单词是由一个单词要素后面跟着0个或者更多个单词要素或者数字要素。
11、合并流SequenceInputStream
SequenceInputStream会将与之相连接的流集组合成一个输入流并从第一个输入流开始读取,直到到达文件末尾,接着从第二个输入流读取,依次类推,直到到达包含的最后一个输入流的末尾为止。 合并流的作用是将多个源合并合一个源。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String filepath1 = "file1.txt"; String filepath2 = "file2.txt"; java.io.Writer w = null; try { w = new FileWriter(filepath1); w.write("百世山河任凋换,一生意气未改迁。愿从劫火投身去,重自寒灰飞赤鸾。\r\n"); w.write("沧海桑田新几度,月明还照旧容颜。琴心剑魄今何在,留见星虹贯九天。 \n"); w.write("冰轮腾转下西楼,永夜初晗凝碧天。长路寻仙三山外,道心自在红尘间。 \n"); w.write("何来慧剑破心茧,再把貂裘换酒钱。回望天涯携手处,踏歌重访白云间。\n"); w.flush();// 把缓冲区内的数据刷新到磁盘 } finally { if (w != null) { w.close();// 关闭流 } } try { w = new FileWriter(filepath2); w.write("何以飘零去,何以少团栾,何以别离久,何以不得安? "); w.flush();// 把缓冲区内的数据刷新到磁盘 } finally { if (w != null) { w.close();// 关闭流 } } java.io.Reader r = null; try { Vector v = new Vector (2); InputStream s1 = new FileInputStream(filepath1); InputStream s2 = new FileInputStream(filepath2); v.addElement(s1); v.addElement(s2); r = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new SequenceInputStream(v.elements()))); char[] data = new char[256]; int len = -1; while ((len = r.read(data)) != -1) {// -1 表示读取到达文件结尾 //操作数据 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { System.out.print(data[i]); } } } finally { if (r != null) { r.close();// 关闭流 } } }
更多Demo: